Logistics refers to the movement, storage and distribution of goods, from their initial production through final delivery. Logistics involves many people, organizations, activities, information, and companies that make goods available for sale. A logistics supply network is a collaborative effort of multiple stakeholders. Although logistics is the main focus of many companies' operations, the process can incorporate other components such as transport and software. Here are the main types of logistical software. These systems can be used to improve the supply chain operations of your company. Continue reading for more information.
Logistics is the movement and storage of goods from their initial production through final delivery.
Logistics is about the efficient movement or storage of products, starting with initial production and ending with final delivery. Optimizing flow ensures that products reach customers at the correct time, at the right place and at the right price. Here are 7 rights of logistics. One of these is the right time. Customers must receive their products on time, in the correct condition, and without any delays.
Inbound logistics is concerned with the inbound movement and product to manufacturers. Outbound logistics, on the other hand, is concerned with the outbound flow and goods from outside the business. Inbound logistics is about acquiring materials, arranging inbound transport, storage, distribution, and delivery to customers. Reverse logistic deals with return shipment of finished goods and their packaging. Some cases may include reusable packaging and disposal.
It is an ad-hoc business.
A risk-adjusted or RAR investment is an investment that has more risk than a normal business investment. The opportunity cost to risk is the difference between the yields of normal business investments and risk-adjusted ones. In addition to reducing the risk of investments, RAR can help business owners manage their cash flows across different functional areas of the business.
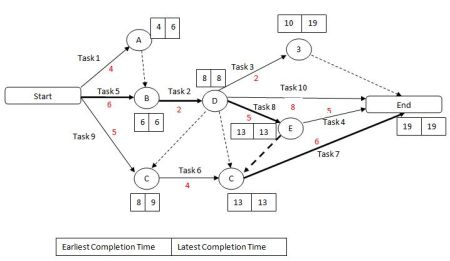
It's a small piece of a larger, collaborative supply network
A highly integrated supply chain is an interdependent network that relies on timely deliveries. In such a chain, failure to deliver could bring the whole chain to a halt. Every disruption can be prevented by even the most reliable suppliers and logistic providers. It is important that all parties evaluate the risks associated with any system in order to ensure that the entire chain runs smoothly and efficiently.
Manufacturers and retailers can collaborate to benefit both sides. For example, a recent collaboration between a retailer and a large U.S. retail chain resulted in a reduced logistics cost between the factory and the store. This collaboration can also increase retailers' sales. Manufacturers can also collaborate with retailers to lower transportation and labor costs.
It involves software
Software that manages supply chains can be used to help companies. Software handles all aspects in the supply chain, including vendor relationships and transactions. Whether you are running a small business or a large corporation, supply chain management software is a necessity. These software can help you manage inventory and supplier relationships as well as flow of data within your company. These programs can cover all stages of product development including warehousing, shipping, and distribution. These programs may include inventory management and insight on trends and customer demand.

Logistic software is used to streamline communication, improve inventory management, and real-time fleet management. It can also improve customer services. It automates daily tasks and turns data into actionable insights for business owners. It also improves communication and inventory processes, which is essential for the successful management of supply chains. These applications can help you improve customer service and increase profitability. You might be curious about the benefits of purchasing software for your business.
FAQ
How can a manager improve his/her managerial skills?
You can improve your management skills by practicing them at all times.
Managers must monitor the performance of subordinates constantly.
You must quickly take action if your subordinate fails to perform.
You should be able to identify what needs improvement and how to improve things.
What are management concepts?
Management Concepts are the management principles and practices that managers use in managing people and resources. These include topics such as human resource policies and job descriptions, performance assessments, training programs and employee motivation.
What kind of people use Six Sigma?
Six-sigma will be well-known to anyone who has worked in operations research or statistics. But anyone can benefit from it.
It is a commitment-intensive task that requires strong leadership skills.
What are the main styles of management?
There are three main management styles: participative, laissez-faire and authoritarian. Each style has its strengths and weaknesses. Which style do you prefer? Why?
Autoritarian – The leader sets the direction for everyone and expects them to follow. This style is best when the organization has a large and stable workforce.
Laissez-faire - The leader allows each individual to decide for him/herself. This style works best when an organization is small and dynamic.
Participative: The leader listens to everyone's ideas and suggestions. This approach works best in small organizations where everyone feels valued.
Statistics
- UpCounsel accepts only the top 5 percent of lawyers on its site. (upcounsel.com)
- Hire the top business lawyers and save up to 60% on legal fees (upcounsel.com)
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
- 100% of the courses are offered online, and no campus visits are required — a big time-saver for you. (online.uc.edu)
- As of 2020, personal bankers or tellers make an average of $32,620 per year, according to the BLS. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
How can you implement Quality Management Plan (QMP).
QMP (Quality Management Plan) is a system to improve products and services by implementing continuous improvement. It provides a systematic approach to improving processes, products and customer satisfaction by continuously measuring, analysing, controlling, controlling, and improving them.
The QMP is a standard method used to ensure good business performance. QMP helps improve production, service delivery and customer relationships. QMPs must include all three elements - Products, Services, and Processes. When the QMP includes only one aspect, it is called a "Process" QMP. If the QMP is focused on a product/service, it's called a QMP. QMP stands for Customer Relationships.
There are two key elements to implementing a QMP: Strategy and Scope. They are defined as follows:
Scope is what the QMP covers and how long it will last. This scope can be used to determine activities for the first six-months of implementation of a QMP in your company.
Strategy: These are the steps taken in order to reach the goals listed in the scope.
A typical QMP is composed of five phases: Planning Design, Development, Implementation and Maintenance. The following describes each phase.
Planning: This stage identifies and prioritizes the QMP's objectives. To get to know the expectations and requirements, all stakeholders are consulted. Next, you will need to identify the objectives and priorities. The strategy for achieving them is developed.
Design: This stage is where the design team creates the vision, mission and strategies necessary for successful implementation of QMP. These strategies are then put into practice by creating detailed plans.
Development: Here the development team works toward building the necessary resources and capabilities to support the successful implementation.
Implementation: This refers to the actual implementation or the use of the strategies planned.
Maintenance: Maintaining the QMP over time is an ongoing effort.
Several additional items should be added to the QMP.
Participation by Stakeholders is essential for the QMP's continued success. They need to be actively involved in the planning, design, development, implementation, and maintenance stages of the QMP.
Project Initiation: It is essential to have a clear understanding about the problem and the solution before you can initiate a project. Also, the initiator should understand why they are doing it and what they expect.
Time Frame: The time frame of the QMP is very critical. If you plan to implement the QMP for a short period, you can start with a simple version. For a long-term commitment you may need more complicated versions.
Cost Estimation: Cost estimation is another vital component of the QMP. Without knowing how much you will spend, planning is impossible. Cost estimation is crucial before you begin the QMP.
QMPs are not only a document, but also a living document. This is the most important aspect of QMPs. It changes with the company. It should therefore be reviewed frequently to ensure that the organization's needs are met.